500 BC – Ancient Greek poet Simonides of Ceos develops what is now known as the method of loci: a memory technique that world memory champions can use to remember pi to 70,000 digits.
300 BC – Philosophers Plato and Aristotle put forward the first theories of memory, describing it as something akin to etchings on a wax tablet.
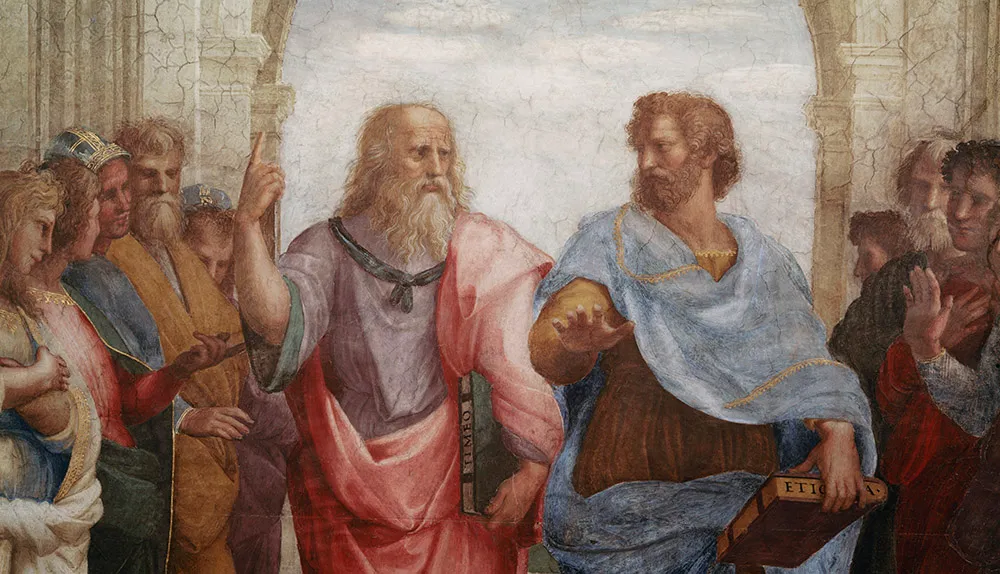

Hermann Ebbinghaus (1850-1909) created a series of nonsense words that provided a way of testing different aspects of memory and forgetting, leading to early definitions of sensory, short-term and long-term memory.

Donald Hebb (1904-1985) proposed that brain cells that are active at the same time form new and stronger connections – a theory that is now known to underlie our ability to create long-term memories.
Read more about memory:
- Where do memories form and how do we know?
- Memory and the brain – the key discovery
- What happens in your brain when you make a memory?
1906 – Physicians Santiago Ramón y Cajal and Camillo Golgi share a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on staining techniques that provided the first clear images of individual neurons.
Wilder Penfield (1891-1976) used electrical currents to stimulate the brain during surgery while his patients were awake. He discovered that you could evoke a memory merely by stimulating parts of the cortex.

Henry Molaison (1926-2008) – After having both sides of his hippocampus removed in an attempt to cure his epilepsy, Molaison experienced profound amnesia. He became one of neuroscience’s most studied individuals, providing key insights into where memories are stored in the brain.
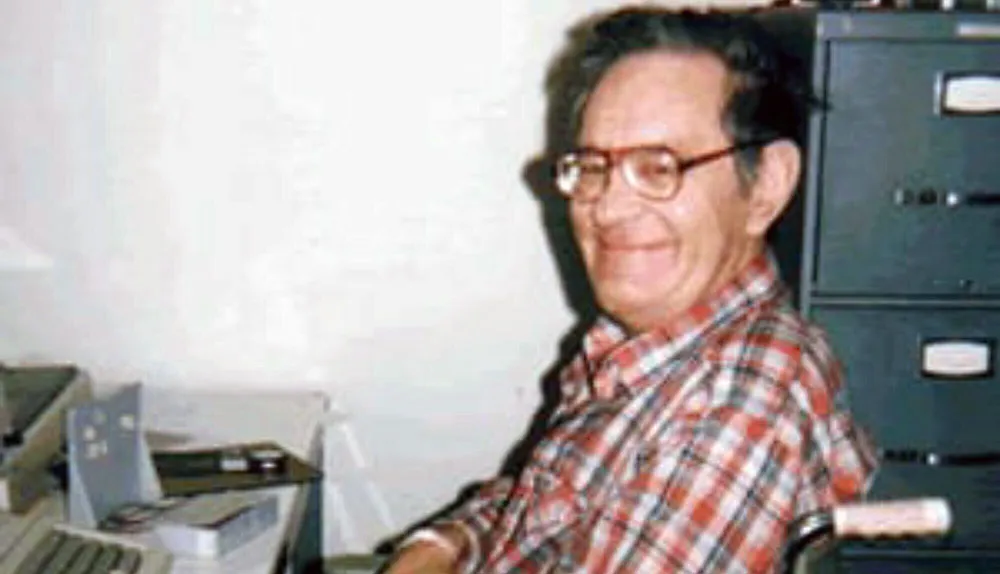

1990s – Throughout the 1990s, Elizabeth Loftus and her colleagues demonstrate the malleability of memory, specifically how false memories can be implanted in our minds.
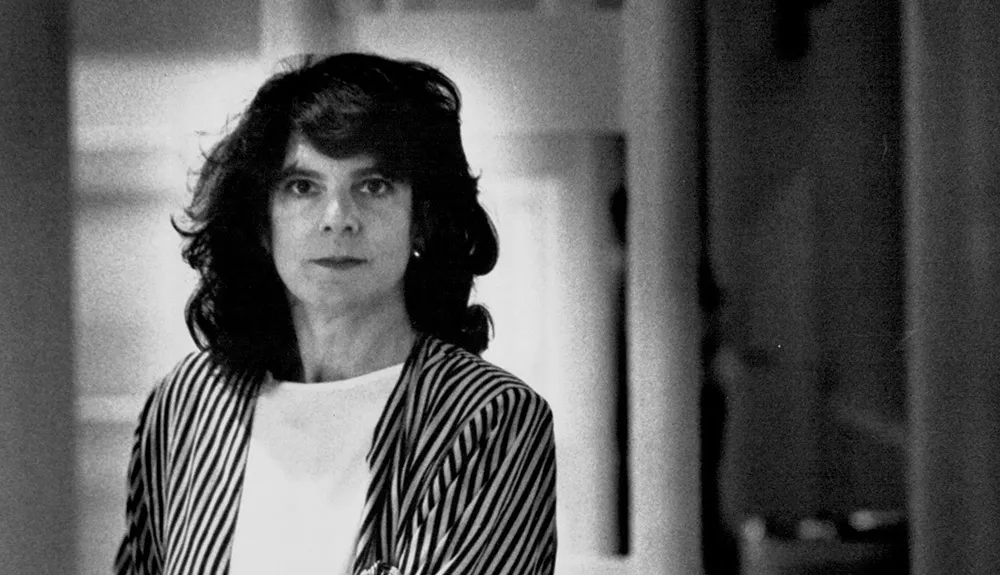

2002 – Neuroscientist Eleanor Maguire scanned the world’s best memorisers and found their brains did not differ from anyone else’s. They were better at remembering because they used a mnemonic device called the method of loci.
2017 – Researchers use optogenetics to discover that long-term memories are created in the brain at the same time as short-term memories, overturning a decades-old theory of how long-term memories form.
- This article first appeared in issue 314 of BBC Focus magazine
