1869 – Friedrich Miescher discovers DNA in his preparations of white blood cells extracted from the pus in surgical bandages. He calls it ‘nuclein’.
1912-14 – William Henry Bragg and son William Lawrence Bragg lay the foundations for the field of X-ray crystallography when they realise they can infer the structure of crystals from the patterns of scattered X-rays.

1920s – Phoebus Levene discovers nucleotides – the combination of a sugar, base and phosphate group – and suggests they form short lengths of DNA called ‘tetranucleotides’.
1937 – Florence Bell arrives in William Astbury’s lab and takes the first X-ray images of DNA. Astbury makes an attempt at a structure the following year.
1944 – Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod and Maclyn McCarty demonstrate that DNA is the material controlling inheritance.
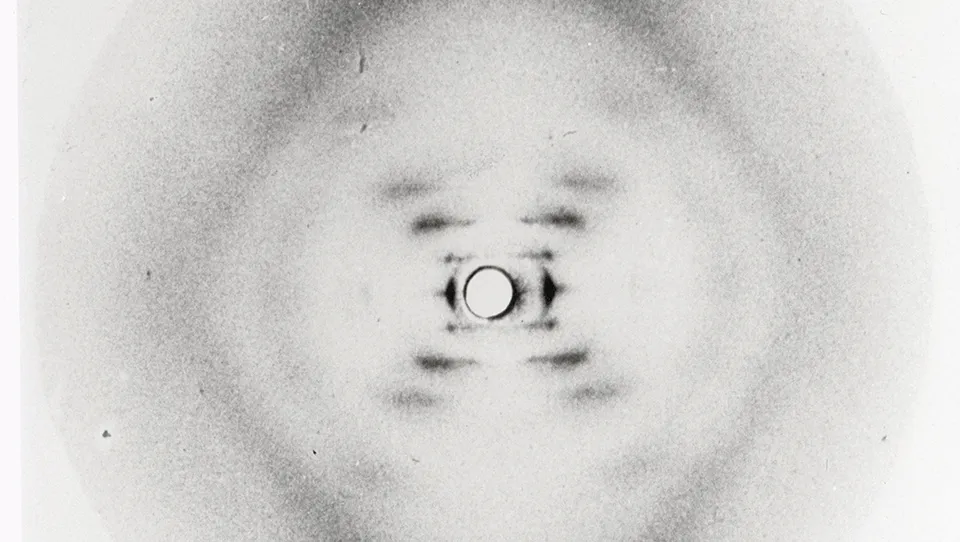
1952 – Rosalind Franklin takes ‘Photo 51’, a highly detailed image of the ‘B’ or hydrated form of DNA. The photo is later seen by James Watson without her knowledge.
Read more about the discovery of DNA:
- How we unravelled the structure of DNA
- Photo 51: the key discovery behind the structure of DNA
- Understanding DNA: Five key scientists who unravelled the helix
- Who really discovered DNA?
1953 – James Watson and Francis Crick propose a model for the structure of the DNA molecule.
They publish the structure in the scientific journal Nature and suggest that the structure indicates DNA’s function.

1972 – DNA from two different organisms is spliced together for the first time by Paul Berg, paving the way for genetic modification and GM foods.
1996 – Dolly the sheep is born. Dolly is the first mammal cloned from a non-embryonic cell. Her DNA is identical to the sheep she was cloned from.
2003 – After £3bn and 13 years of work, the Human Genome Project is completed and the entire genome of a human being is published. Today, people can get their genome sequenced in a matter of hours for around £100.

2015 – President Barack Obama announced plans to sequence the genomes of one million US citizens to help personalise medicine and learn more about rare diseases.