Nebulae are clouds of dust and gas that represent either end of a star’s life cycle. Some are places where stars have died, otherswherestars are forming. The Orion Nebula is the latter.
At only 1,344 light-years away, the Orion Nebula is the closest and one of the brightest nebulae visible from Earth. This means it can be seen with the naked eye up to mid-March when viewed under dark skies.
The brightness of objects in the night sky as seen from Earth are measured on a logarithmic scale:the lower the number,the brighter the object. This scale means an object with magnitude 1 will be10times brighter than a magnitude 2 object. The Sun has a magnitude of -26, while the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius, has a magnitude of -1.46.
The Orion Nebula has a magnitude of 4, which means it is fairly faint – you’ll have to go somewhere dark and let your eyes adjust to really see it. It’s best to pick a night with no moonlight such as during a new Moon.
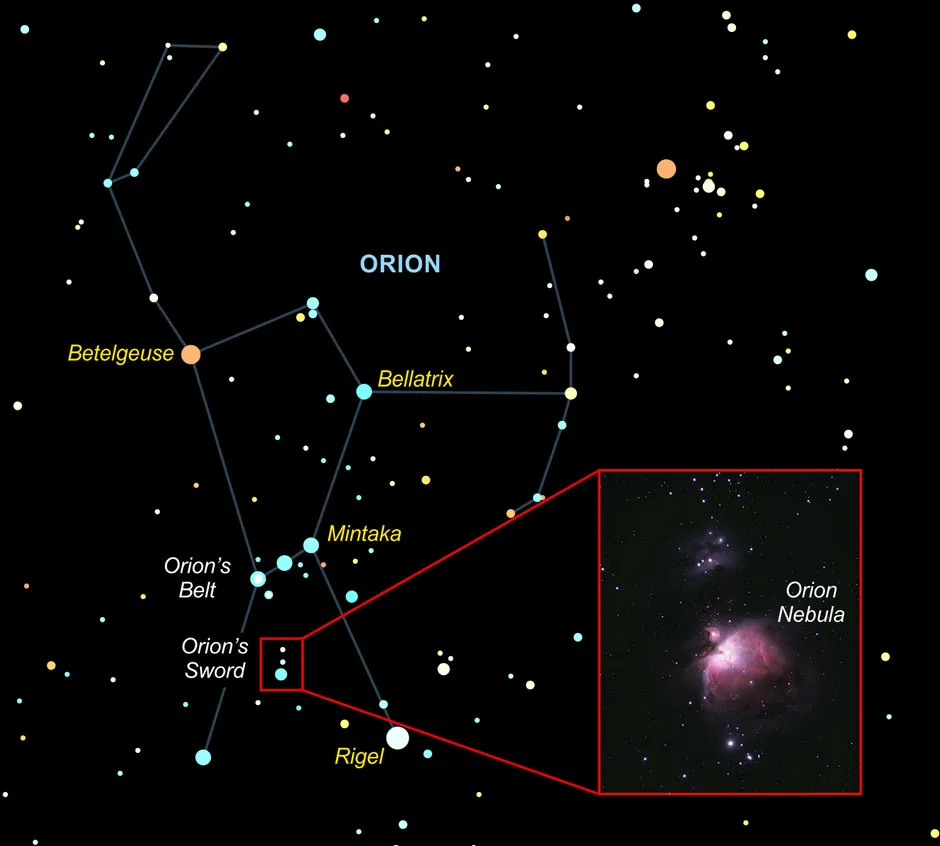
Finding the Orion Nebula is easy as it is in the constellation Orion, one of the most easily recognisable constellations. In February and early March, Orion will be visible in the eastern skyas soon as theSun sets, sweeping south in the northern hemisphere then setting in the west in the early hours of the morning. In the southern hemisphere, Orion will be visible in the north, appearing upside-down compared to how it looks in the northern hemisphere.
To find the nebula, look below the three stars of Orion’s Belt (or above, if viewing from the southern hemisphere). You will see a faint line of stars, whichmake upOrion’s sword. The nebula is halfway down the sword and will appear as a fuzzy-lookingstar.
Looking for stargazing tips? Check out our complete astronomy for beginners UK guide.
Read more:
- How can I see the Pleiades star cluster?
- How can I see Betelgeuse?
- How can I see the Andromeda Galaxy?
- How can I spot the International Space Station?
To submit your questions email us at questions@sciencefocus.com (don't forget to include your name and location)

